The goal of this notebook is to code a decision tree classifier/regressor that can be used with the following API:
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv")
train_df, test_df = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2)
tree = decision_tree_algorithm(train_df, ml_task="regression")
accuracy = calculate_accuracy(test_df, tree)
The algorithm that is going to be implemented looks like this:
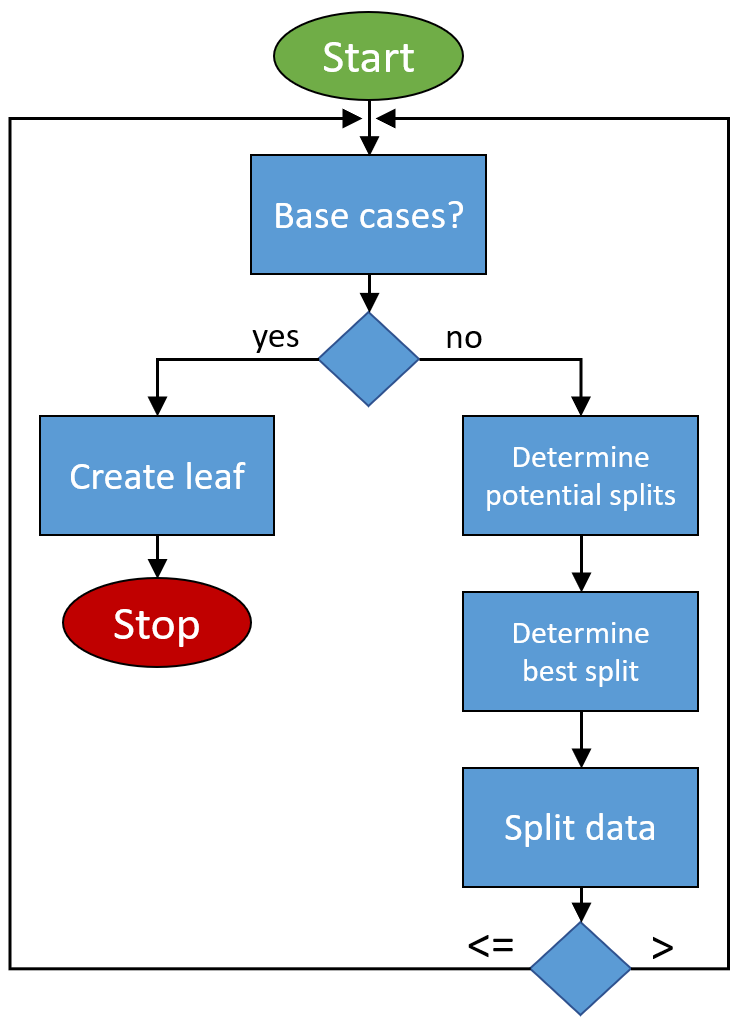
Import Statements¶
In [1]:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import random
from pprint import pprint
In [2]:
%matplotlib inline
sns.set_style("darkgrid")
Load and Prepare Data¶
Format of the data¶
- the last column of the data frame must contain the label and it must also be called "label"
- there should be no missing values in the data frame
In [3]:
df = pd.read_csv("../data/Bike.csv", parse_dates=["dteday"])
df = df.drop(["instant", "casual", "registered"], axis=1)
df = df.rename({"dteday": "date"}, axis=1)
In [4]:
df.head()
Out[4]:
In [5]:
date_column = df.date
df["day_of_year"] = date_column.dt.dayofyear
df["day_of_month"] = date_column.dt.day
df["quarter"] = date_column.dt.quarter
df["week"] = date_column.dt.week
df["is_month_end"] = date_column.dt.is_month_end
df["is_month_start"] = date_column.dt.is_month_start
df["is_quarter_end"] = date_column.dt.is_quarter_end
df["is_quarter_start"] = date_column.dt.is_quarter_start
df["is_year_end"] = date_column.dt.is_year_end
df["is_year_start"] = date_column.dt.is_year_start
df = df.set_index("date")
In [6]:
df["label"] = df.cnt
df = df.drop("cnt", axis=1)
In [7]:
df.head()
Out[7]:
Train-Val-Test-Split¶
In [8]:
train_df = df.iloc[:-122]
val_df = df.iloc[-122:-61] # Sep and Oct of 2012
test_df = df.iloc[-61:] # Nov and Dec of 2012
Helper Functions¶
The helper functions operate on a NumPy 2d-array. Therefore, let’s create a variable called “data” to see what we will be working with.
In [9]:
data = train_df.values[:5]
data
Out[9]:
Data pure?¶
In [10]:
def check_purity(data):
label_column = data[:, -1]
unique_classes = np.unique(label_column)
if len(unique_classes) == 1:
return True
else:
return False
Create Leaf¶
In [11]:
def create_leaf(data, ml_task):
label_column = data[:, -1]
if ml_task == "regression":
leaf = np.mean(label_column)
# classfication
else:
unique_classes, counts_unique_classes = np.unique(label_column, return_counts=True)
index = counts_unique_classes.argmax()
leaf = unique_classes[index]
return leaf
Potential splits?¶
In [12]:
def get_potential_splits(data):
potential_splits = {}
_, n_columns = data.shape
for column_index in range(n_columns - 1): # excluding the last column which is the label
values = data[:, column_index]
unique_values = np.unique(values)
potential_splits[column_index] = unique_values
return potential_splits
Split Data¶
In [13]:
def split_data(data, split_column, split_value):
split_column_values = data[:, split_column]
type_of_feature = FEATURE_TYPES[split_column]
if type_of_feature == "continuous":
data_below = data[split_column_values <= split_value]
data_above = data[split_column_values > split_value]
# feature is categorical
else:
data_below = data[split_column_values == split_value]
data_above = data[split_column_values != split_value]
return data_below, data_above
Determine Best Split¶
In [14]:
def calculate_mse(data):
actual_values = data[:, -1]
if len(actual_values) == 0: # empty data
mse = 0
else:
prediction = np.mean(actual_values)
mse = np.mean((actual_values - prediction) **2)
return mse
In [15]:
def calculate_entropy(data):
label_column = data[:, -1]
_, counts = np.unique(label_column, return_counts=True)
probabilities = counts / counts.sum()
entropy = sum(probabilities * -np.log2(probabilities))
return entropy
In [16]:
def calculate_overall_metric(data_below, data_above, metric_function):
n = len(data_below) + len(data_above)
p_data_below = len(data_below) / n
p_data_above = len(data_above) / n
overall_metric = (p_data_below * metric_function(data_below)
+ p_data_above * metric_function(data_above))
return overall_metric
In [17]:
def determine_best_split(data, potential_splits, ml_task):
first_iteration = True
for column_index in potential_splits:
for value in potential_splits[column_index]:
data_below, data_above = split_data(data, split_column=column_index, split_value=value)
if ml_task == "regression":
current_overall_metric = calculate_overall_metric(data_below, data_above, metric_function=calculate_mse)
# classification
else:
current_overall_metric = calculate_overall_metric(data_below, data_above, metric_function=calculate_entropy)
if first_iteration or current_overall_metric <= best_overall_metric:
first_iteration = False
best_overall_metric = current_overall_metric
best_split_column = column_index
best_split_value = value
return best_split_column, best_split_value
Decision Tree Algorithm¶
Representation of the Decision Tree¶
In [18]:
sub_tree = {"question": ["yes_answer",
"no_answer"]}
In [19]:
example_tree = {"petal_width <= 0.8": ["Iris-setosa",
{"petal_width <= 1.65": [{"petal_length <= 4.9": ["Iris-versicolor",
"Iris-virginica"]},
"Iris-virginica"]}]}
Determine Type of Feature¶
In [20]:
def determine_type_of_feature(df):
feature_types = []
n_unique_values_treshold = 15
for feature in df.columns:
if feature != "label":
unique_values = df[feature].unique()
example_value = unique_values[0]
if (isinstance(example_value, str)) or (len(unique_values) <= n_unique_values_treshold):
feature_types.append("categorical")
else:
feature_types.append("continuous")
return feature_types
Algorithm¶
In [21]:
def decision_tree_algorithm(df, ml_task, counter=0, min_samples=2, max_depth=5):
# data preparations
if counter == 0:
global COLUMN_HEADERS, FEATURE_TYPES
COLUMN_HEADERS = df.columns
FEATURE_TYPES = determine_type_of_feature(df)
data = df.values
else:
data = df
# base cases
if (check_purity(data)) or (len(data) < min_samples) or (counter == max_depth):
leaf = create_leaf(data, ml_task)
return leaf
# recursive part
else:
counter += 1
# helper functions
potential_splits = get_potential_splits(data)
split_column, split_value = determine_best_split(data, potential_splits, ml_task)
data_below, data_above = split_data(data, split_column, split_value)
# check for empty data
if len(data_below) == 0 or len(data_above) == 0:
leaf = create_leaf(data, ml_task)
return leaf
# determine question
feature_name = COLUMN_HEADERS[split_column]
type_of_feature = FEATURE_TYPES[split_column]
if type_of_feature == "continuous":
question = "{} <= {}".format(feature_name, split_value)
# feature is categorical
else:
question = "{} = {}".format(feature_name, split_value)
# instantiate sub-tree
sub_tree = {question: []}
# find answers (recursion)
yes_answer = decision_tree_algorithm(data_below, ml_task, counter, min_samples, max_depth)
no_answer = decision_tree_algorithm(data_above, ml_task, counter, min_samples, max_depth)
# If the answers are the same, then there is no point in asking the qestion.
# This could happen when the data is classified even though it is not pure
# yet (min_samples or max_depth base case).
if yes_answer == no_answer:
sub_tree = yes_answer
else:
sub_tree[question].append(yes_answer)
sub_tree[question].append(no_answer)
return sub_tree
In [22]:
tree = decision_tree_algorithm(train_df, ml_task="regression", max_depth=3)
pprint(tree)
Prediction¶
In [23]:
sub_tree
Out[23]:
In [24]:
example = test_df.iloc[0]
example
Out[24]:
In [25]:
def predict_example(example, tree):
question = list(tree.keys())[0]
feature_name, comparison_operator, value = question.split(" ")
# ask question
if comparison_operator == "<=":
if example[feature_name] <= float(value):
answer = tree[question][0]
else:
answer = tree[question][1]
# feature is categorical
else:
if str(example[feature_name]) == value:
answer = tree[question][0]
else:
answer = tree[question][1]
# base case
if not isinstance(answer, dict):
return answer
# recursive part
else:
residual_tree = answer
return predict_example(example, residual_tree)
In [26]:
predict_example(example, tree)
Out[26]:
Hyperparameter Tuning¶
In [27]:
def calculate_r_squared(df, tree):
labels = df.label
mean = labels.mean()
predictions = df.apply(predict_example, args=(tree,), axis=1)
ss_res = sum((labels - predictions) ** 2)
ss_tot = sum((labels - mean) ** 2)
r_squared = 1 - ss_res / ss_tot
return r_squared
The following cell takes some time to run!!!
In [28]:
grid_search = {"max_depth": [], "min_samples": [], "r_squared_train": [], "r_squared_val": []}
for max_depth in range(1, 7):
for min_samples in range(5, 20, 5):
tree = decision_tree_algorithm(train_df, ml_task="regression", max_depth=max_depth, min_samples=min_samples)
r_squared_train = calculate_r_squared(train_df, tree)
r_squared_val = calculate_r_squared(val_df, tree)
grid_search["max_depth"].append(max_depth)
grid_search["min_samples"].append(min_samples)
grid_search["r_squared_train"].append(r_squared_train)
grid_search["r_squared_val"].append(r_squared_val)
print(f"Progress: Iteration {max_depth}/6")
grid_search = pd.DataFrame(grid_search)
grid_search.sort_values("r_squared_val", ascending=False).head()
Out[28]:
Visualization¶
In [29]:
best_max_depth = 6
best_min_samples = 15
tree = decision_tree_algorithm(train_df, ml_task="regression", max_depth=best_max_depth, min_samples=best_min_samples)
calculate_r_squared(test_df, tree)
Out[29]:
In [30]:
def create_plot(df, tree, title):
predictions = df.apply(predict_example, args=(tree,), axis=1)
actual = df.label
plot_df = pd.DataFrame({"actual": actual, "predictions": predictions})
plot_df.plot(figsize=(18, 5), title=title)
return
In [31]:
create_plot(train_df, tree, title="Training Data")
In [32]:
create_plot(train_df, tree, title="Training Data")
plt.xlim(pd.to_datetime("2011-01-01"), pd.to_datetime("2011-02-28"));
In [33]:
create_plot(val_df, tree, title="Validation Data")
In [34]:
create_plot(test_df, tree, title="Test Data")
Classification Task¶
In [35]:
df = pd.read_csv("../data/Iris.csv")
df = df.drop("Id", axis=1)
df = df.rename(columns={"species": "label"})
In [36]:
df.head()
Out[36]:
In [37]:
def train_test_split(df, test_size):
if isinstance(test_size, float):
test_size = round(test_size * len(df))
indices = df.index.tolist()
test_indices = random.sample(population=indices, k=test_size)
test_df = df.loc[test_indices]
train_df = df.drop(test_indices)
return train_df, test_df
In [38]:
random.seed(0)
train_df, test_df = train_test_split(df, test_size=20)
In [39]:
tree = decision_tree_algorithm(train_df, ml_task="classification", max_depth=3)
pprint(tree)
In [40]:
def calculate_accuracy(df, tree):
df["classification"] = df.apply(predict_example, args=(tree,), axis=1)
df["classification_correct"] = df["classification"] == df["label"]
accuracy = df["classification_correct"].mean()
return accuracy
In [41]:
accuracy = calculate_accuracy(test_df, tree)
accuracy
Out[41]:
In [ ]: